How to Create Docker Containers in AWS?
We continue our AWS related blog series that we started in our first article Use AWS services as building blocks to implement your enterprise system. In this new article we talk about our experiences regarding how to create Docker containers in AWS.
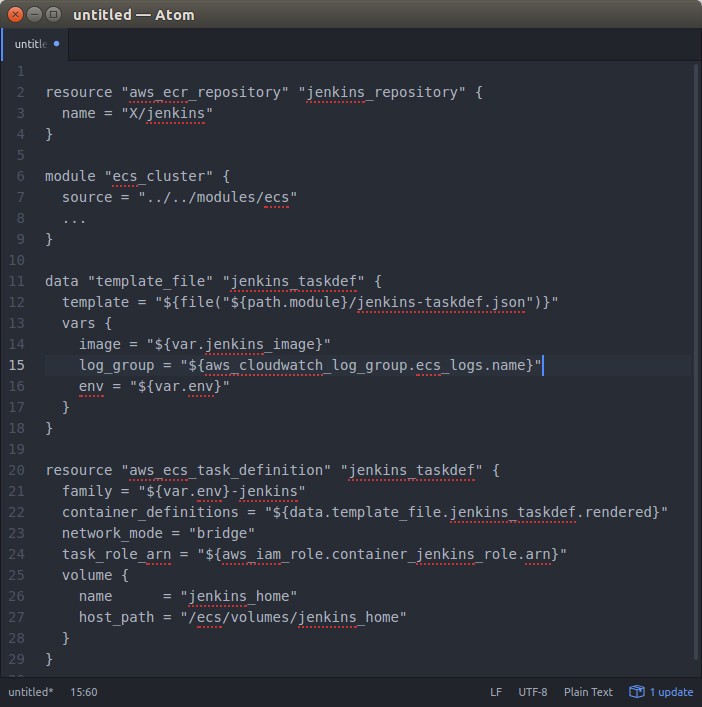
Example ECS Terraform configuration.
Introduction
In our previous blog posts How to Create EC2 Images in AWS? and How to Create Lambdas in AWS? we already explained that there are several ways to create services to AWS infrastructure: EC2 instances (servers), Docker containers and Lambdas (serverless functionality).
This blog post is a short introduction how to create Docker containers for Amazon Web Services.
What Are Docker Containers?
A Docker image is a lightweight layered image that utilizes services in the host OS. A Docker container is a runnable Docker image. This blog post assumes that the reader knows basics about Docker containers, if not read more in the Docker home page.
Docker is an excellent way to build functionality to AWS since you can develop the functionality in a local Docker container and test the container locally before deploying the Docker image to AWS. Using Docker testing the deployable functionality is really fast since the Docker container boots in milliseconds. And if you use Linux you can use Docker natively (ohoi Tieto developers — another good reason to install Tubuntu; see: Tubuntu — Rebel Without a Cause).
We have used Docker containers with AWS e.g. to run Jenkins CI server, to gather analytics for AWS Elasticsearch etc.
How to Create a Docker Container?
This blog post assumes that the reader knows basics about Docker. In this blog post we use Jenkins Docker container as an example. Let’s briefly list the most important steps to create your own Jenkins Docker container:
- Create a Dockerfile in which you base your own image to either some basic Linux image (in which case you need to install also Jenkins itself) or standard Jenkins Docker image. We chose standard Jenkins Docker image.
- Install all software you need (e.g. Java8…) using Dockerfile.
- Create a plugins.txt file in which you define which plugins to install to Jenkins. Instruct Jenkins (in Dockerfile) to do the installation.
- Start Docker container locally, check that Jenkins works, and commit container to a new image if you did any tweaking to Jenkins using browser.
How to Create and Deploy Docker Containers to AWS?
AWS provides an EC2 Container Service for hosting Docker containers. In practice first you create an EC2 Container Registry (ECR) and you deploy your Docker image to that repository. We have used for all AWS related configurations our favorite Infrastructure as Code tool Terraform (see also our previous blog article How to Create and Manage Resources in Amazon Web Services Infrastructure?). The code snippet picture in the beginning of this article shows an example how to configure ECS using Terraform.
After setting up the registry you create an EC2 Container Service Cluster (see above mentioned picture). The cluster configuration can be a bit complex, in the example above we have most of the complexities in a dedicated custom tailored Terraform module called “ecs”. The idea of the ECS is to host the docker containers which are called “Tasks” in ECS terminology.
Create an ECS task definition file in which you define e.g. log group, container port forwardings, mount point for ebs volume etc. Basically you define the same container/host configurations as you would do when running containers in a Linux host + some AWS additions.
Deploy your Docker image to ECR. This step involves authenticating to ECR and pushing your image to ECR.
Once everything is ready you should have an ECR registry with your image and an ECS instance (basically an EC2 virtual server, you can see it in the EC2 dashboard). Start your task in the ECS, create ssh tunnel to the EC2 instance (to the port you forwarded in the ECS Task…) open browser and test that you see Jenkins welcome page.
The actual process involves quite a few bits and pieces — we have listed in this article only the most important high level steps. You should consult Docker / AWS documentation for details. If you are a Tieto developer and need assistance how to use Docker containers, Lambdas or EC2 in AWS you are welcome to consult the writers.
Conclusion
There are many ways to create application services to AWS infrastructure. When you want to develop and test functionality quickly in your own development machine before deployment you can use Docker containers and AWS EC2 Container Service.
Both writers are AWS Certified Solution Architects Associate, architecting and implementing AWS projects in Tieto CEM Finland. If you are interested about starting a new AWS project in Finland, you can contact us with firstname.lastname at tieto.com.
Kari Marttila & Timo Tapanainen
Kari Marttila’s Home Page in LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/karimarttila/
Timo Tapanainen’s Home Page in LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/timo-tapanainen/
